KCA News & Media
Press Release
Press Release
| Control Over Wet Wipes Needed | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | 2016-09-23 | Hit | 3039 | ||
|
Control Over Wet Wipes Needed - Some Wet Tissue Products Dissatisfy Safety and Labelling Standard -
Wet wipes are widely used among many consumers. Not only do they have easy access - at supermarket or convenience store, for instance - but also help keep hands and body clean. Nonetheless, concerns over chemical products for daily use are on the rise, reinforcing necessity for providing information to consumers.
Korea Consumer Agency (www.kca.go.kr) analysed injury information in regard to the wet wipes, conducted germicide test, preserved agent test, and microorganisms test on 27 wet wipes for personal hygiene, and inspected labelling of the products. Based on discoveries, the KCA issued safety alert for preventing consumer injury. * Wet wipes for babies and children (15 kinds), wet wipes for general use (4 kinds).
□ Annual increases in report on injuries incurred by wet wipes, especially on foreign materials and decomposition Consumer Injury Surveillance System (CISS) received 210 reports on the products from 2013 to June 2016 in total, and the number is steadily growing every year. * 46 cases in 2013 → 66 cases in 2014 → 50 cases in 2015 → 48 cases in 1H, 2016
The reports on foreign materials such as insects and scum account for 38.6% (81 cases), the biggest share of the total. Reports on decomposition are 33.8% (71 cases), on irritated skin after use are 12.4% (26 cases), on chemicals-related issues are 7.1% (15 cases), on bad odour are 4.8% (10 cases), on containers are 1.4% (3 cases) and on others are 1.9% (4 cases).
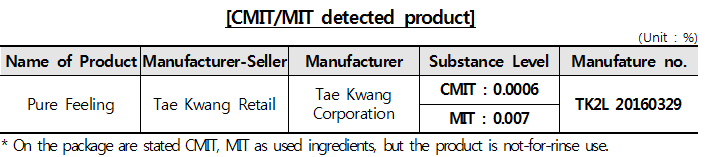
□ CMIT, MIT detected product in market Wet wipes for personal hygiene, originally categorised as manufactured product, have been labelled as cosmetic product since July 2015. Thus the goods must satisfy the safety standards prescribed in Cosmetics Act.
Regarding the result of the germicide/preserved agent test, all the objects meet the safety standard except one that turns out to have CMIT and MIT. The current Cosmetics Act prohibits CMIT or MIT compounds to be used in cosmetics apart from products that must be washed away (below 0.0015% level of the substances) due to concerns over skin sensitisation after use above the level. * adverse skin reaction such as rubefaction and allergic reaction to cosmetics
※ Unlike South Korea and European countries, CMIT/MIT compounds can be used in cosmetic products in the U.S. and Australia. Japan allows only rinse-after-use products with the chemicals under 0.1% level.
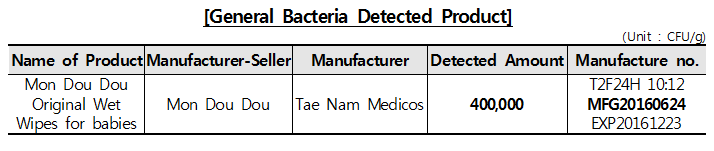
□ Product detected more general bacteria than standard The result of microorganisms test shows that 26 object products was not detected to have bacteria and mycete, except one with 400,000CFU/g of general bacteria which is far exceeding the standard (less than 100CEU/g).
Wet wipes, of which the main ingredient is water, can have contaminated microorganisms proliferated in the course of manufacture and distribution. Therefore, manufacturers and manufacture-sale managers must prevent contamination of microorganisms through safety and hygiene control.
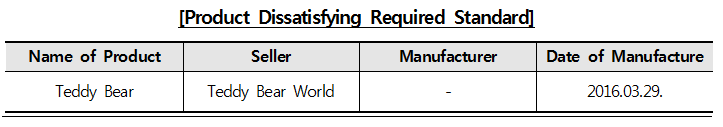
□ Product dissatisfying standard for matters required to be stated in packages of cosmetics For labelling information, 26 in 27 objects have all required matters stated on the packages under Cosmetics Act, but only one product has matters stated in accordance to Quality Control and Safety Management of Industrial Products Act, the formerly applied rule.
□ Intensified control on safety matters required to be stated needed along with consumers’ following instruction for safe use. In order to prevent further consumer injury and assure safety of wet wipes, the KCA has sent a notice of recommendation of correction to the manufactures/sellers to recall the products that violate the standards. The businesses accepted the notice, recalled the products that do not meet the safety standards, or halted the sales of the products that do not have matters statement required. The KCA plans to request Ministry of Food and Drug Safety of the Republic of Korea to reinforce control on safety and information statement for wet wipes in the market.
Furthermore, in order to assure consumer safety, the KCA suggests guidelines for safe use of wet wipes as consumer information, such as to use them within 1 to 3 months after opening and to check the ingredients stated on the packages. It also advised consumers regarding cosmetic products that they have to check the ingredients when they buy cosmetics manufactured before the date of implementation of rules related to CMIT/MIT compounds (11 August 2015), because those products may contain such materials.
|
|||||
| Next | Excessive Damages for Breach of Contract for Overseas Travel and Frequent Change in Itinerary | ||||
| Prev | Mobile Easy Payment Service Needs More Affiliated Shops and Additional Services | ||||